The working principle of the slitter machine in different stages
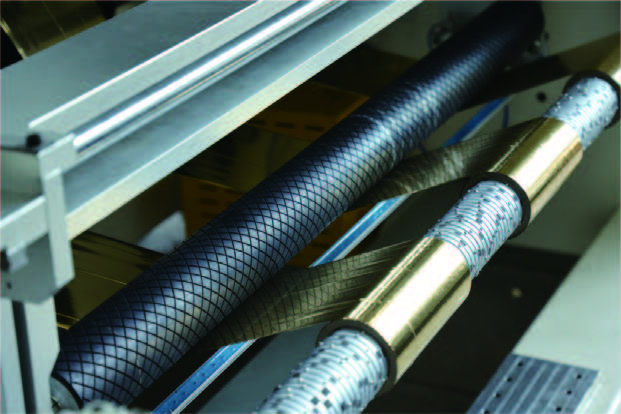

A slitting machine is a commonly used industrial equipment used to cut materials such as paper, plastic film, cloth, etc. according to the required size and shape. Let's take a look at how the slitting machine works at different stages.
The working principle of the slitter in different stages is as follows:
1. Feeding stage:
At this stage, the raw material, usually a continuous supply of rolled material, is directed through a feeding system to the working area of the slitter.
Feeding systems typically include rollers, clamps, or clamping devices to stabilize the movement of the raw material and ensure that it moves to the next stage in the correct position and speed.
2. Positioning stage:
At this stage, the raw material is precisely positioned to ensure accuracy and consistency in the cut.
Positioning systems may include sensors, vision systems, or mechanical positioning devices that detect and adjust the position and orientation of raw materials.
3. Cutting stage:
This is the main working stage of the slitter machine, in which the raw material is cut into multiple parts according to the desired size and shape.
Cutting is usually done with a cutter, cutterhead, or scoring wheel, and the cutter can be rotating or stationary, adjusting as needed to achieve different cuts.
4. Discharge stage:
After the cutting is completed, the cut parts are discharged from the slitter machine for subsequent processing or packaging stages.
The discharge system typically includes a conveyor belt, pusher, or robotic arm that removes the cut part from the slitter and transfers it to the next station.
The entire process is usually managed by an automated control system to ensure efficient, precise, and consistent slitting operations. At the same time, operators may need to monitor and adjust the operating parameters of the slitter to meet specific production needs and quality standards.
Recent Post
 Energy Optimization for Film Slitters: Which Designs Reduce Electricity Costs?
Energy Optimization for Film Slitters: Which Designs Reduce Electricity Costs? How to improve the working efficiency of slitting and rewinding machine?
How to improve the working efficiency of slitting and rewinding machine? Smooth and burr-free slitting edges? Tension control and blade optimization for ribbon slitter
Smooth and burr-free slitting edges? Tension control and blade optimization for ribbon slitter Barcode ribbon slitter operation guide: from beginner to proficient
Barcode ribbon slitter operation guide: from beginner to proficient
 350mm Mini Slittting Machine
350mm Mini Slittting Machine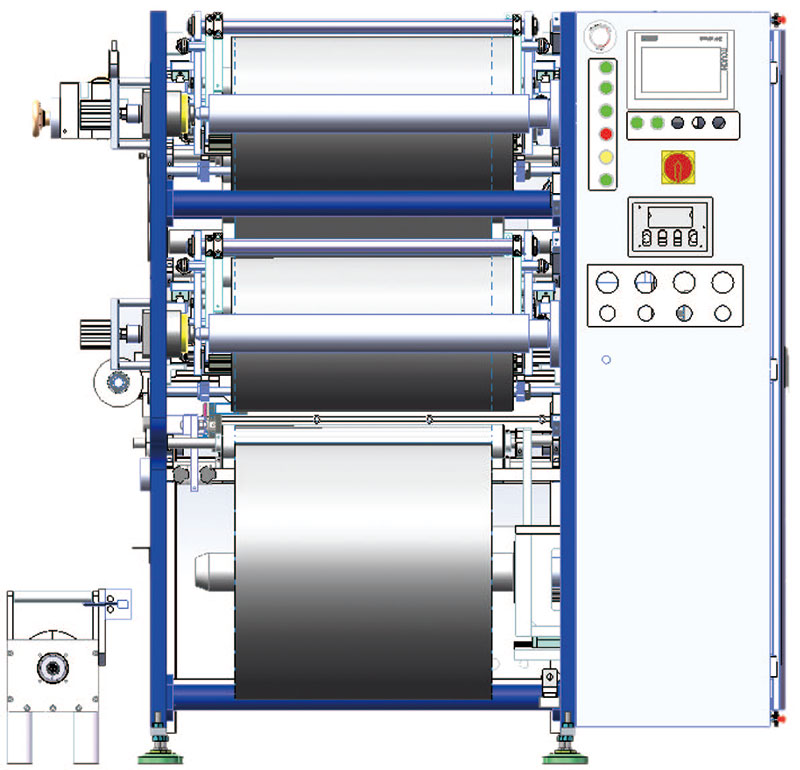 Customerized Slitter
Customerized Slitter Label Slitting Machine
Label Slitting Machine 450S Mini Slittting Machine
450S Mini Slittting Machine 250mm Mini Slittting Machine
250mm Mini Slittting Machine 450mm Mini Slittting Machine
450mm Mini Slittting Machine Barcode Ribbon Slitting Machine
Barcode Ribbon Slitting Machine 300S Mini Slittting Machine
300S Mini Slittting Machine